CBSE Class 12 Chemistry – MCQ and Online Tests – Unit 11 – Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Every year CBSE conducts board exams for 12th standard. These exams are very competitive to all the students. So our website provides online tests for all the 12th subjects. These tests are also very effective and useful for those who preparing for competitive exams like NEET, JEE, CA etc. It can boost their preparation level and confidence level by attempting these chapter wise online tests.
These online tests are based on latest CBSE Class 12 syllabus. While attempting these our students can identify the weak lessons and continuously practice those lessons for attaining high marks. It also helps to revise the NCERT textbooks thoroughly.
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry – MCQ and Online Tests – Unit 11 – Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Question 1.
Order of esterification of alcohols are
(a) 3° > 1° > 2°
(b) 2°> 3° > 1°
(c) 1 ° > 2° > 3°
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) 1 ° > 2° > 3°
Question 2.
What happens when tertiary butyl alcohol is passed over heated copper at 300°C?
(a) Secondary butyl alcohol is formed
(b) 2-methylpropene is formed
(c) 1-butene is formed
(d) Butanol is formed
Answer
Answer: (b) 2-methylpropene is formed
Question 3.
Which of the follow ing compounds will be most easily attacked by an electrophile?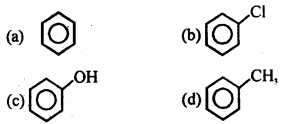
Answer
Answer: (c)
Question 4.
The decreasing order of boiling point of the following alcohols is
(a) 3-methylbuan-2-ol > 2-methylbutan-2-ol > pentan-1-ol
(b) Pentan-1-ol > 3-methylbutan-2-ol > 2-methylbutan-2-ol
(c) 2-methylbutan-2-ol > 3-methylbutan-2-ol > pentan-1-ol
(d) 2-methylbutan-2-ol > pental-1-ol > 3-methylbutan-2-ol
Answer
Answer: (b) Pentan-1-ol > 3-methylbutan-2-ol > 2-methylbutan-2-ol
Question 5.![]()
In the reaction, X is
(a) (CH3)2C = CHCH3
(b) CH3C = CH
(c) (CH3)2CHCH2CH3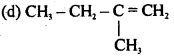
Answer
Answer: (a) (CH3)2C = CHCH3
Ans. a
Question 6.
What would be the reactant and reagent used to obtain 2, 4-dimenthyl pentan-3-ol?
(a) Propanal and propyl magnesium bromide
(b) 3-methylbutanal and 2-methyl magnesium iodide
(c) 2-dimethylpropanone and methyl magnesium odide
(d) 2-methylpropanal and isopropyl magnesium iodide
Answer
Answer: (d) 2-methylpropanal and isopropyl magnesium iodide
Question 7.
Vapours of an alcohol X when passed over hot reduced copper, produce an alkene, the alcohol is
(a) primary alcohol
(b) secondary alcohol
(c) tertiary alcohol
(d) dihydric alcohol
Answer
Answer: (c) tertiary alcohol
Question 8.
Acid catalysed dehydration of t-butanol is faster than that of n-butanol because
(a) tertiary carbocation is more stable than primary carbocation
(b) primary carbocation is more stable than tertiary carbocation
(c) t-butanol has a higher boiling point
(d) rearrangement takes place during dehydration of t- butanol
Answer
Answer: (a) tertiary carbocation is more stable than primary carbocation
Question 9.
An unknown alcohol is treated with “Lucas reagent” to determine whether the alcohol is primary, secondary or tertiary. Which alcohol reacts fastest and by what mechanism?
(a) Tertiary alcohol by SN2
(b) Secondary alcohol by SN1
(c) Tertiary alcohol by SN1
(d) Secondary alcohol by SN2
Answer
Answer: (c) Tertiary alcohol by SN1
Question 10.
Which of the following alcohols reacts most readily with Lucas reagent?
(a) CH3CH2CH2OH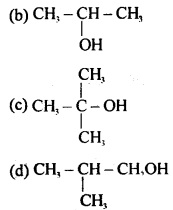
Answer
Answer: (c)
Question 11.
Picricacid is a yellow coloured compound. Its chemical name is
(a) m-nitrobenzoic acid
(b) 2, 4, 6-trinitropheriol
(c) 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol
(d) p-nitrophenol
Answer
Answer: (b) 2, 4, 6-trinitropheriol
Question 12.
One mole of ethyl acetate on tatment with an excess of LiAlH4 in dry ether and subsequent acidification produces
(a) 1 mole acetic acid + 1 mole ethyl alcohol
(b) 1 mole ethyl alcohol + 1 mole methyl alcohol
(c) 2 moles of ethyl alcohol
(d) 1 mole of 2-butanol
Answer
Answer: (c) 2 moles of ethyl alcohol
Question 13.
Which of the following alcohols gives 2-butenc on dehydration byconc. H2SO4?
(a) 2-methyl propene-2-ol
(b) 2-methyl 1 -propanol
(c) Butane-2-ol
(d) Butane 1-ol
Answer
Answer: (c) Butane-2-ol
Question 14.
Phenol when treated with excess of bromine water gives a white precipitate of
(a) 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol
(b) o-bromophenol
(c) p-bromophenol
(d) bromobenzene
Answer
Answer: (a) 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol
Question 15.
Ortho-nitrophenol is less soluble in water than, p- and m- nitrophenols because
(a) o-nitrophenol shows intramolecular H-bonding
(b) o-nitrophenol shows intermolecular H-bonding
(c) melting point of o-nitrophenol is lower than those of m- and p-isomers
(d) o-nitrophenol is more volatile in steam than those of m- and p-isomers
Answer
Answer: (a) o-nitrophenol shows intramolecular H-bonding
Question 16.
Which of the following alcohol is dehydrated most easily with cone. H2SO4?
(a) p-O2NC6H4CH(OH)CH3
(b) p-ClC6H4CH(OH)CH3
(c) p-CH3OC6H4CH(OH)CH3
(d) C6H5CH(OH)CH3
Answer
Answer: (c) p-CH3OC6H4CH(OH)CH3
Question 17.
The best reagent to convert pent-3-en-2-ol into pent-3-en- 2-one is
(a) acidic permanganate
(b) acidic dichromate
(c) chromic anhydride in glacial acetic acid
(d) pyridiriium chlorochromate
Answer
Answer: (d) pyridiriium chlorochromate
Question 18.
Identify the final product of the reaction sequence.![]()
(a) Benzophenone
(b) Acetophenone
(c) Diphenyl
(d) Methyl salicylate
Answer
Answer: (b) Acetophenone
Question 19.
Propanone on reaction with alkyl magnesium bromide followed by hydrolysis will produce
(a) primary alcohol
(b) secondary alcohol
(c) tertiary alcohol
(d) carboxylic acid
Answer
Answer: (c) tertiary alcohol
Question 20.
Arrange the following alcohols in order of increasing reactivity towards sodium metal.
(i) (CH3)3C-OH
(ii) (CH3)2CH-OH
(iii) CH3CH2OH
(a) (iii) < (ii) < (i)
(b) (ii) > (i) < (iii)
(c) (i) < (ii) < (iii)
(d) (iii) < (i) < (ii)
Answer
Answer: (c) (i) < (ii) < (iii)
Question 21.
An alcohol X when treated with hot cone. H2SO4 gave an alkene Y with formula C4H8. This alkene on ozonolysis gives single product with molecular formula C2H4O. The alcohol is
(a) butan-1-ol,
(b) butan-2-ol
(c) 2-methylpropan-1-ol
(d) 2,2-dimethylbutynal-1-oI
Answer
Answer: (b) butan-2-ol
Question 22.
The reaction between phenol and chloroform in the presence of aqueous NaOH is
(a) nucleophilic substitution reaction
(b) electrophilic addition reaction
(c) electrophilic substitution reaction
(d) nucleophilic addition reaction
Answer
Answer: (c) electrophilic substitution reaction
Question 23.
In the following reaction sequence Z is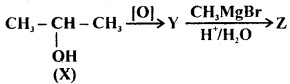
(a) butan-1-ol
(b) butan-2-ol
(c) 2-methylpropan-2-ol
(d) 1, 1-dimethylethanol
Answer
Answer: (c) 2-methylpropan-2-ol
Question 24.
The most suitable reagent for the conversion of RCH2OH → RCHO is
(a) K2Cr2O7
(b) CrO3
(c) KMnO4
(d) PCC
Answer
Answer: (d) PCC
Question 25.
Which of the following reagents can not, be used to oxidise primary alcohols to aldehydes?
(a) CrO3 in anhydrous medium
(b) KMnO4 in acidic medium
(c) Pyridinium chlorochromate
(d) Heat in the presence of Cu at 573 K
Answer
Answer: (b) KMnO4 in acidic medium
Question 26.
1-Phenylethanol can be prepared by the reaction of benzaldehyde with
(a) methyl bromide
(b) ethyl iodide and magnesium
(c) methyl iodide and magnesium (Grignard reagent’s)
(d) methyl bromide and aluminium bromide
Answer
Answer: (c) methyl iodide and magnesium (Grignard reagent’s)
Question 27.
Benzoquinone is prepared by reaction of phenol with
(a) Na2Cr2O7, H2SO4
(b) KMnO4, H2SO4
(c) Na2CrO4,HCl
(d) K2MnO4, H2SO4
Answer
Answer: (a) Na2Cr2O7, H2SO4
Question 28.
The major product obtained on interaction of phenol with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide is
(a) benzoic acid
(b) salicyaldehyde
(c) salicylic acid
(d) phthalic acid
Answer
Answer: (c) salicylic acid
Question 29.
Tertiary butyl alcohol gives tertiary butyl chlorideon treatment with
(a) Conc HCl/anhydrous ZnCl3
(b) KCN
(c) NaOCl
(d) Cl2
Answer
Answer: (a) Conc HCl/anhydrous ZnCl3
Question 30.
Conversion of phenol to salicyclic acid and to salicyaldehyde are known as (respectively)
(a) Reimer-Tiemann reaction and Kolbe’s reaction
(b) Williamson’s synthesis and Hydrobration-oxidation
(c) Kolbe’s reaction and Williamson’s synthesis
(d) Kolbe’s reaction and Reimer-Tiemann reaction
Answer
Answer: (d) Kolbe’s reaction and Reimer-Tiemann reaction
Question 31.
Which of the following alcohols will give the most stable carbocation during dehydration?
(a) 2-methyl-1-propanol
(b) 2-methyl-2-propanol
(c) 1-Butanol
(d) 2-Butanol
Answer
Answer: (b) 2-methyl-2-propanol
Question 32.
The major product of acid catalysed dehydration of 2-methylcyclohexanol and butan-1-ol are respectively
(a) 1 -methylcyclohexene andbut-1-ene
(b) 2-methylcyclohexene and but-2-ene
(c) 2-methylcyclohexene and butane
(d) 1-methylcyclohexene and but-2-ene
Answer
Answer: (a) 1 -methylcyclohexene andbut-1-ene
Question 33.
Which of the following is phenol?
(a) Cresol
(b) Catechol
(c)Benzenol
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (d) All of these
Question 34.
Which of the following compounds will give tribromo derivative on treatment with bromine water?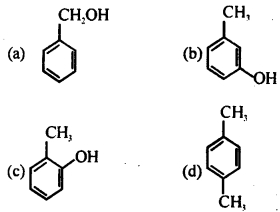
Answer
Answer: (b)
Question 35.
A compound X with the molecular formula C2H8O can be oxidised to another compound Y whose molecular formulae is C3H6O2. The compound X may be
(a) CH3CH2OCH3
(b) CH3CH2CHO
(c) CH3CH2CH2OH
(d) CH3CHOHCH3
Answer
Answer: (c) CH3CH2CH2OH













0 Comments:
Post a Comment