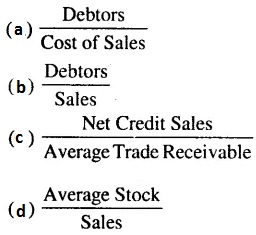
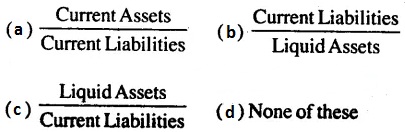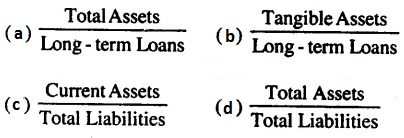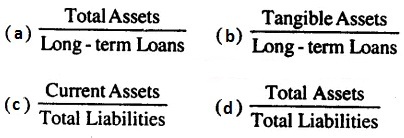CBSE Class 12 Accountancy – MCQ and Online Tests – Unit 9 – Analysis of Financial Statements
Every year CBSE conducts board exams for 12th standard. These exams are very competitive to all the students. So our website provides online tests for all the 12th subjects. These tests are also very effective and useful for those who preparing for competitive exams like NEET, JEE, CA etc. It can boost their preparation level and confidence level by attempting these chapter wise online tests.
These online tests are based on latest CBSE Class 12 syllabus. While attempting these our students can identify the weak lessons and continuously practice those lessons for attaining high marks. It also helps to revise the NCERT textbooks thoroughly.
CBSE Class 12 Accountancy – MCQ and Online Tests – Unit 9 – Analysis of Financial Statements
Question 1.
Common-size Statement are also known as:
(a) Dynamic Analysis
(b) Horizontal Analysis
(c) Vertical Analysis
(d) External Analysis
Answer
Answer: (c) Vertical Analysis
Question 2.
The most commonly used tools for financial analysis are:
(a) Comparative Statements
(b) Common-size Statement
(c) Accounting Ratios
(d) All the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 3.
Tools for comparison of financial statements are :
(a) Comparative Balance Sheet
(b) Comparative Income Statement
(c) Common-size Statement
(d) All the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 4.
Comparative Financial Statements show:
(a) Financial position of a concern
(b) Earning capacity of a concern
(c) Both of them
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) Both of them
Question 5.
Common-size financial statements are mostly prepared:
(a) In proportion
(b) In percentage
(c) (a) and (b) both
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) In percentage
Question 6.
Which of the following is not a limitations of financial statement analysis ?
(a) To measure the financial strength
(b) Affected by window-dressing
(c) Do not reflect changes in price level
(d) Lack of Qualitative Analysis
Answer
Answer: (a) To measure the financial strength
Question 7.
Tangible assets of company increased from T 4,00,000 to T 5,00,000. What is the percentage of change ?
(a) 20%
(b) 25%
(c) 33%
(d) 50%
Answer
Answer: (b) 25%
Question 8.
Horizontal Analysis is also known as :
(a) Dynamic Analysis
(b) Structural Analysis
(c) Static Analysis
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Dynamic Analysis
Question 9.
Which of the following shows the actual financial position of n enterprise ?
(a) Fund Flow
(b) Balance Sheet
(c) P & L A/c
(d) Ratio Analysis
Answer
Answer: (b) Balance Sheet
Question 10.
A company’s net sales are ₹ 15,00,000; cost of sales is ₹ 10,00,000 and indirect expenses are ₹ 3,00,000, the amount gross profit will be:
(a) ₹ 13,00,000
(b) ₹ 5,00,000
(c) ₹ 2,00,000
(d) ₹ 12,00,000
Answer
Answer: (c) ₹ 2,00,000
Question 11.
If total assets of a firm are 7 12,00,000 and its non of non-current assets to total assets ?
(a) 50%
(b) 75%
(c) 25%
(d) 80%
Answer
Answer: (b) 75%
Question 12.
Which of the following is the purpose or objective of financial analysis ?
(a) To assess the current profitability of the firm
(b) To measure the solvency of the firm
(c) To assess the short-term and long-term liquidity position of the firm
(d) All the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 13.
Financial analysis is significant because it:
(a) Ignores qualitative aspect
(b) Judges operational efficiency
(c) Suffers from the limitations of financial statements
(d) It is affected by personal ability and bias of the analysis
Answer
Answer: (b) Judges operational efficiency
Question 14.
If total assets of a firm are 7 10,00,000 and its non-current assets are 7 6,00,000, what will be the percentage of current assets on total assets ?
(a) 60%
(b) 50%
(c) 40%
(d) 30%
Answer
Answer: (c) 40%
Question 15.
Break-even point refers to that point where :
(a) Total Costs are more than Total Sales
(b) Total Costs are less than Total Sales
(c) Total Costs are half of the Total Sales
(d) Total Cost are equal to total sales
Answer
Answer: (d) Total Cost are equal to total sales
Question 16.
Payment of Income Tax is considered as :
(a) Direct Expenses
(b) Indirect Expenses
(c) Operating Expenses
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Indirect Expenses
Question 17.
Which of these are not the method of financial statement analysis ?
(a) Ratio Analysis
(b) Comparative Analysis
(c) Trend Analysis
(d) Capitalisation Method
Answer
Answer: (d) Capitalisation Method
Question 18.
In a common-size Balance Sheet, total equity and liabilities are assumed to be equal to :
(a) 1,000
(b) 100
(c) 10
(d) 1
Answer
Answer: (b) 100
Question 19.
Interpretation of Financial Statements includes:
(a) Criticisms and Analysis
(b) Comparison and Trend Study
(c) Drawing Conclusion
(d) All the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 20.
Break-even Analysis shows:
(a) Relationship between cost and sales
(b) Relationship between production and purchases
(c) Relationship between cost and revenue
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Relationship between cost and sales
Question 21.
Sales less Cost of goods sold is called :
(a) Operating Profit
(b) Gross Profit
(c) Net Profit
(d) Total Profit
Answer
Answer: (b) Gross Profit
Question 22.
Trend ratios and trend percentage are used in :
(a) Dynamic analysis
(b) Static analysis
(c) Horizontal analysis
(d) Vertical Analysis
Answer
Answer: (c) Horizontal analysis
Question 23.
In which meeting of company directors report is presented ?
(a) Directors Meeting
(b) Annual General Meeting
(c) Manager’s Meeting
(d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) Annual General Meeting
Question 24.
Analysis of financial statements involve :
(a) Trading A/c
(b) Profit & Loss statement
(c) Balance Sheet
(d) All the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 25.
Comparative financial analysis process shows the comparison between the items of which statement:
(a) Balance Sheet
(b) Profit & Loss Statement
(c) (a) and (b) both
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) (a) and (b) both
Question 26.
What is shown by Balance Sheet ?
(a) Accuracy of books of accounts
(b) Profit or loss of a specific period
(c) Financial position on a specific date
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Financial position on a specific date
Question 27.
A company’s shareholders fund was 7 8,00,000 in the year 2015. It because 7 12,00,000 in the year 2016. What is percentage of change ?
(a) 100%
(b) 25%
(c) 50%
(d) 33.3%
Answer
Answer: (c) 50%
Question 28.
The financial statements of a business enterprise include:
(a) Balance Sheet
(b) Profit & Loss Account
(c) Cash Flow Statement
(d) All the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 29.
An annual report is issued by company to its :
(a) Directors
(b) Auditors
(c) Shareholders
(d) Management
Answer
Answer: (c) Shareholders
Question 30.
The analysis of financial statement by a shareholder is an example of:
(a) External Analysis
(b) Internal Analysis
(c) Vertical Analysis
(d) Horizontal Analysis
Answer
Answer: (a) External Analysis
Question 31.
Financial analysis is useful:
(a) For Investors
(b) For Shareholders
(c) For Debenture holders
(d) All the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 32.
Balance Sheet provides information about financial position of the enterprise :
(a) At a Point of Time
(b) Over a Period of Time
(c) For a Period of Time
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) At a Point of Time
Question 33.
Profit & Loss Account is also called :
(a) Balance Sheet
(b) Income Statements
(c) Operating Profit
(d) Investment
Answer
Answer: (b) Income Statements
Question 34.
Vertical Analysis is also known as :
(a) Fluctuation Analysis
(b) Static Analysis
(c) Horizontal Analysis
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Static Analysis
Question 35.
Which of the following statement is correct ?
(a) Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders funds
(b) Assets = Total funds
(c) Assets = Funds of outsiders .
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders funds
Question 36.
What is shown by the Income Statement ?
(a) Accuracy of books of accounts
(b) Profit or loss of a certain period
(c) Balance of Cash Book
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Profit or loss of a certain period
Question 37.
Out of the following which parties are interested in financial statements ?
(a) Managers
(b) Financial Institutions
(c) Creditors
(d) All the these
Answer
Answer: (d) All the these
Question 38.
Financial analysis is significant because it:
(a) Ignores qualitative aspect
(b) Judges operational efficiency
(c) Suffers from the limitations of financial statements
(d) It is affected by personal ability and bias of the analysis
Answer
Answer: (b) Judges operational efficiency
Question 39.
Comparative Statements are also known as :
(a) Dynamic Analysis
(b) Horizontal Analysis
(c) Vertical Analysis
(d) External Analysis
Answer
Answer: (b) Horizontal Analysis