CBSE Class 11 Chemistry – MCQ and Online Tests – Unit 11 – The p-Block Elements
Every year CBSE schools conducts Annual Assessment exams for 6,7,8,9,11th standards. These exams are very competitive to all the students. So our website provides online tests for all the 6,7,8,9,11th standard’s subjects. These tests are also very effective and useful for those who preparing for any competitive exams like Olympiad etc. It can boost their preparation level and confidence level by attempting these chapter wise online tests.
These online tests are based on latest CBSE syllabus. While attempting these our students can identify the weak lessons and continuously practice those lessons for attaining high marks. It also helps to revise the NCERT textbooks thoroughly.
CBSE Class 11 Chemistry – MCQ and Online Tests – Unit 11 – The p-Block Elements
Question 1.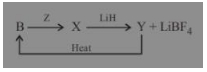
Which of the statement is true for the above sequence of reactions?
(a) Z is hydrogen
(b) X is B2H6
(c) Z and Y are F2 and B2H6 respectively
(d) Z is Potassium Hydroxide
Answer
Answer: (c) Z and Y are F2 and B2H6 respectively
Explanation:
F2(Z) LiH
B(s) ? BF3 ? B2H6 + LiBF4
(X) (Y)
Question 2.
Ammonia gas can be dried by
(a) conc H2SO4
(b) P2O5
(c) CaCl2
(d) Quick lime
Answer
Answer: (d) Quick lime
Explanation:
Ammonia, with H2SO4 forms ammonium sulphate, with CaCl2 forms CaCl2.8NH3 and with P2O5 gives NH4PO3, hence these reagents cannot be used for drying ammonia.
Question 3.
Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Copper (I) metaborate is colourless
(b) Copper (II) metaborate is colourless
(c) Copper (II) metaborate is light green
(d) Copper (I) metaborate is dark green
Answer
Answer: (a) Copper (I) metaborate is colourless
Explanation:
Copper (II) metaborate is bluish green and colour of Copper (I) metaborate is blue in colour.
Question 4.
The structure of diBorane contains
(a) Four 2c – 2e bonds and two 3c – 2e bonds
(b) Two 2c – 2e bonds and two 3c – 2e bonds
(c) Two 2c – 2e bonds and two 3c – 3e bonds
(d) Four 2c – 2e bonds and four 3c – 2e bonds
Answer
Answer: (a) Four 2c – 2e bonds and two 3c – 2e bonds
Explanation:
According to molecular orbital theory, each of the two boron atoms is in sp³ hybrid state. Of the four hybrid orbitals, three have one electron each while the fourth is empty. Two of the four orbitals of each of the boron atom overlap with two terminal hydrogen atoms forming two normal B – H s-bonds. One of the remaining hybrid orbital (either filled or empty) of one of the boron atoms, 1s orbital of hydrogen atoms (bridge atom) and one of hybrid orbitals of the other boron atom overlap to form a delocalised orbital covering the three nuclei with a pair of electrons. Such a bond is known as three centre two electron (3c – 2e) bonds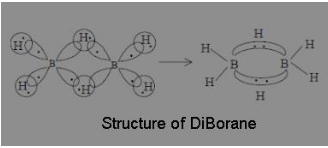
Question 5.
Which is not the correct statement for Boron?
(a) It exhibits Allotropy
(b) It exists in both crystalline and Amorphous form
(c) It forms solid chlorides
(d) It forms volatile hydrides.
Answer
Answer: (c) It forms solid chlorides
Explanation:
Boron exists in amorphous and crystalline state and exhibit allotropy.
It forms numerous volatile hydrides which spontaneously catch fire on exposure to air and are easily hydrolysed.
The chlorides of Boron is liquid, it fumes in most air and readily hydrolysed by water.
Question 6.
Oxygen gas can be prepared from solid KMnO4 by:
(a) Dissolving the solid in dil. HCl
(b) Dissolving the solid in conc. H2SO4
(c) Treating the solid with H2 gases
(d) Strongly heating the solid
Answer
Answer: (d) Strongly heating the solid
Explanation:
Oxygen gas can be prepared from solid KMnO4
250°C
2KMnO4 ? KMnO4 + MnO2 + O2
Question 7.
In the upper layers of atmosphere ozone is formed:
(a) By action of electric discharge on oxygen molecule
(b) By action of ultraviolet rays on oxygen molecule
(c) By action of infrared rays on oxygen molecule
(d) Due to sudden drops of pressure
Answer
Answer: (b) By action of ultraviolet rays on oxygen molecule
Explanation:
In the upper layer of atmosphere, the Ultraviolet rays (UV rays) split the molecule of oxygen (O2) into its constituent 2 atoms.
Each of the atom then combine with another oxygen (O2) molecule which gives rise to Ozone (O3).
Question 8.
Among the C-X bond (where, X = Cl, Br, l) the correct decreasing order of bond energy is
(a) C-I > C-Cl > C-Br
(b) C-I > C-Br > C-Cl
(c) C-Cl > C-Br > C-I
(d) C-Br > C-Cl > C-I
Answer
Answer: (c) C-Cl > C-Br > C-I
Explanation:
Among the C-X bond (where , X = Cl, Br, I), the correct decreasing order of bond energy is
C-Cl > C-Br > C-l
Question 9.
Which of the following oxidation states are most characteristic for lead and tin respectively?
(a) 2, 2
(b) 4, 2
(c) 2, 4
(d) 4, 4
Answer
Answer: (c) 2, 4
Explanation:
Due to inert pair effect, ns² electron pair of Pb does not participate in bonding. Thus, +2 is the most characteristic oxidation state for Pb. However, for Sn, the inert pair effect is not so strong Thus, +4 is the most characteristic oxidation state for Sn.
Question 10.
When excess of Kl is added to copper sulphate solution:
(a) Cuprous iodide is formed
(b) l2 is liberated
(c) Potassium iodide is oxidized
(d) All
Answer
Answer: (d) All
Explanation:
It is an redox reaction which occurs when the iodide ion will reduce the copper (II) ion to copper(I) while iodide itself is oxidized to elemental iodine. Like most copper (I) compounds, Cul is insoluble in water.
KI + 2CuSO4 (aq) ? Cu2l2(s) + l2(s) + 2K2SO4(aq)
Question 11.
Which of the following statements regarding ozone is not correct?
(a) The oxygen-oxygen bond length in ozone is identical with that of molecular oxygen
(b) The ozone is response hybrid of two structures
(c) The ozone molecule is angular in shape
(d) Ozone is used as a germicide and disinfectant for the purification of air.
Answer
Answer: (a) The oxygen-oxygen bond length in ozone is identical with that of molecular oxygen
Explanation:
The oxygen–oxygen bond length in ozone is identical with that of molecular oxygen
Question 12.
K2[Hgl4] detect the ion/group :
(a) NH2
(b) NO
(c) NH2+
(d) Cl–
Answer
Answer: (c) NH2+
Explanation:
K2[Hgl4], Nesslers reagent detects NH+4 ion.
Question 13.
Red phosphorus is chemically less reactive because
(a) It does not contain P – P bonds
(b) It dos not contain tetrahedral P4 molecules
(c) It does not catch fire in air even upto 400°C
(d) It has a polymeric structure
Answer
Answer: (d) It has a polymeric structure
Explanation:
Red phosphorus is less reactive because of its gaint polymeric structure.
Question 14.
Which of the following will not produce hydrogen gas?
(a) Reaction between Fe and dil. HCl
(b) Reaction between Zn and NaOH
(c) Reaction between Zn and conc. H2SO4
(d) Electrolysis of NaCl in Nelsons cell
Answer
Answer: (c) Reaction between Zn and conc. H2SO4
Explanation:
Concentrated sulphuric acid reacts with Zn to give SO2 and not H2
Question 15.
On heating ozone, its volume.
(a) Increase to 1.5 times
(b) Decreases to half
(c) Remain uncharged
(d) Becomes double
Answer
Answer: (a) Increase to 1.5 times
Explanation:
O3 ? O2 + [O]
1 mole of O3 on heating produces 1 mole of O2 and 1 mole of [O], hence its volume increases to 1.5 times.
Question 16.
In the compound of type ECl3, where E = B, P, As, or Bi, the angle Cl – E – Cl for different E are ion the order:
(a) B > = P = As = Bi
(b) B > P > As > Bi
(c) B < P = As = Bi
(d) B < P < As < Bi
Answer
Answer: (b) B > P > As > Bi
Explanation:
BCl3 is trigonal planar in structure and bond angles are 120° each. PCl3, AsCl3, and BiCl3 are pyramidal in shape with sp³ hybridization.
In all of them, the bond angles are less than the normal tetrahedral angle of 109.28, and also these bond angles decrease down the group. Therefore, the correct order of bond angles is as follows:
B > P > As > Bi
Question 17.
Inert gases such as helium behave like ideal gases over a wide range of temperature .However; they condense into the solid state at very low temperatures. It indicates that at very low temperature there is a
(a) Weak attractive force between the atoms
(b) Weak repulsive force between the atoms
(c) Strong attractive force between the atoms
(d) Strong repulsive attractive between the atoms
Answer
Answer: (c) Strong attractive force between the atoms
Explanation:
Inert gases condense into the solid state at very low temperature as there is strong attractive force between the atoms.
In solid state, Van der Waals attractive forces are predominant between the atoms. The attractive force increases with the size of the atom as a result of the increase in polarizability and the decrease in ionization potential.
Question 18.
In general, the Boron Trihaides act as
(a) Strong reducing agent
(b) Lewis Acids
(c) Lewis Bases
(d) Dehydrating Agents
Answer
Answer: (b) Lewis Acids
Explanation:
The boron atom in trihaldies has only six electrons in the valence shell and hence can accept a pair of electrons in the vacant p-orbital to complete its octet. As a result, boron trihaldies act as a Lewis acids.
Question 19.
Which of the following has least covalent P-H bond?
(a) PH+4
(b) P2H+5
(c) P2H2+6
(d) PH3
Answer
Answer: (c) P2H2+6
Explanation:
The covalent charter of P-H bond depends on the formal charge distributed on each P-H bond
In PH+4 it is +1/4 = +0.25, in P2H+5 it is +1/5 = +0.2 and in P2H62+ it is +2/6 = +0.33.
The higher the formal charge the lesser the covalent character due to more polarisation. Thus the least covalent P-H bond is present in P2H2+64
Question 20.
If Cl2 gas is passed in to aqueous solution of Kl containing some CCl4 and the mixture is shaken then:
(a) Upper layer becomes violet
(b) Lower layer becomes violet
(c) Homogenous violet layer is formed
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Upper layer becomes violet
Explanation:
2KI + Cl2 ? 2KCl l2
I2 CCl4 ? Violet Colour
But the excess of Cl2 should be avoided.
The layer may become colourless due to conversion of I2 to HIO3
I2 + 5Cl2 + 6H2O ? 2HIO3 + 10HCl
In case of Br2
Br2 + 2H2O + Cl2 ? 2HBrO + HCl













0 Comments:
Post a Comment