CBSE Class 11 Chemistry – MCQ and Online Tests – Unit 13 – Hydrocarbons
Every year CBSE schools conducts Annual Assessment exams for 6,7,8,9,11th standards. These exams are very competitive to all the students. So our website provides online tests for all the 6,7,8,9,11th standard’s subjects. These tests are also very effective and useful for those who preparing for any competitive exams like Olympiad etc. It can boost their preparation level and confidence level by attempting these chapter wise online tests.
These online tests are based on latest CBSE syllabus. While attempting these our students can identify the weak lessons and continuously practice those lessons for attaining high marks. It also helps to revise the NCERT textbooks thoroughly.
CBSE Class 11 Chemistry – MCQ and Online Tests – Unit 13 – Hydrocarbons
Question 1.
The first fraction obtained during the fractionation of petroleum is:
(a) Gasoline
(b) Diesel Oil
(c) Hydrocarbon Gases
(d) Kerosene Oil
Answer
Answer: (c) Hydrocarbon Gases
Explanation:
During fractionation or distillation of petroleum, gases light hydrocarbons in the form of gases are obtained from first fraction.
Question 2.
2 – Phenylpropene on acidic hydration gives
(a) 2 – Phenyl – 2 – propanol
(b) 2 – Phenyl – 1 – propanol
(c) 3 – Phenyl – 1 – propanol
(d) 1 – Phenyl – 2 – propanol
Answer
Answer: (a) 2 – Phenyl – 2 – propanol
Explanation:
Acidic hydration of 2-phenyl propene follows electrophilic reaction mechanism forming an intermediate 3° carbocation (more stable), there by forming 2-phenyl-2-propanol.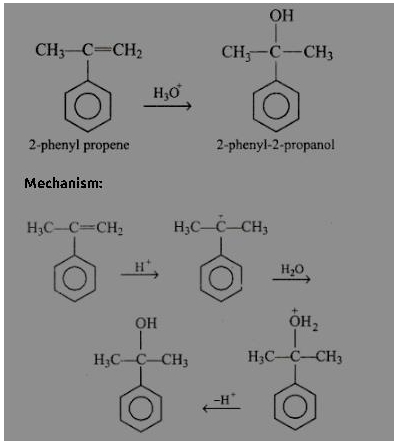
Question 3.
Nitrobenzene on reaction with conc. HNO3/H2SO4 at 80 – 100°C forms which one of the following products?
(a) 1, 2-Dinitrobenzene
(b) 1, 3-Dinitrobenzene
(c) 1, 4-Dinitrobenzene
(d) 1, 2, 4-Trinitrobenzene
Answer
Answer: (b) 1, 3-Dinitrobenzene
Explanation:
NO2 is an m-directing group and hence, 1, 3-dinitrobenzene is formed.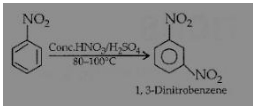
Question 4.
Some meta-directing substituents in aromatic substitution are given. Which one is most deactivating?
(a) –C = N
(b) -SO3H
(c) -COOH
(d) -NO2
Answer
Answer: (d) -NO2
Explanation:
The correct order of deactivation is
-NO2 > -C = N > -SO32 H > -COOH
Question 5.
Which of the following compounds will exhibit geometrical isomerism?
(a) 1 – Phenyl – 2 – butene
(b) 3 – Phenyl – 1 – butene
(c) 2 – Phenyl – 1 butene
(d) 1, 1 – Diphenyl – propene .
Answer
Answer: (a) 1 – Phenyl – 2 – butene
Explanation:
C6H5CH2-CH = CH-CH3 (1-phenyl-2-butene) exhibits the phenomenon of geometrical isomerism due to Cab = Cad structure, so its two isomers are possible which are given are follow :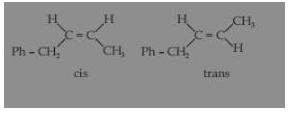
Question 6.
The order of decreasing reactivity towards an electrophilic reagent, for the following : (i) Benzene (ii) Toluene (iii) Chlorobenzene (iv) Phenol would be:
(a) (i) > (ii) > (iii) > (iv)
(b) (ii) > (iv) > (i) > (iii)
(c) (iv) > (iii) > (ii) > (i)
(d) (iv) > (ii) > (i) > (iii)
Answer
Answer: (d) (iv) > (ii) > (i) > (iii)
Explanation:
Benzene having any activating group i.e., OH, R etc., undergoes electrophilic substitution very easily as compared to benzene itself. Thus toluene (C6H5CH3), phenol (C6H5OH) undergo electrophilic substitution very readily than benzene. Chlorine with +E and +M effect deactivates the ring due to strong -I effect. So, it is difficult to carry out the substitution in chlorobenzene than in benzene, so correct order is Phenol (iv) > Toluene (ii) > Benzene (i) > Chlorobenzene (iii)
Question 7.
Pure methane can be prepared by
(a) Soda lime decarboxylation
(b) Kolbes electrolytic method
(c) Wurtz reaction
(d) Reduction with H2
Answer
Answer: (a) Soda lime decarboxylation
Explanation:
Methane cannot be prepared by either Wurtz reaction, Kolbes electrolytic method or by reduction of alkenes with H2. While acetic acid salt on heating with soda lime gives methane.
CH3COONa– ? CH4 + Na2CO3
Question 8.
Isopropyl bromide on Wurtz reaction gives
(a) Hexane
(b) Propane
(c) 2, 3 – Dimethylbutane
(d) Neohexane
Answer
Answer: (c) 2, 3 – Dimethylbutane
Explanation:
CHMe2 – Br + 2Na + Br – CHMe2 + Br – CHMe2 \(\underrightarrow { dryEther } \) Me2CH – CHMe2 + 2NaBr
Question 9.
Nitrobenzene on reaction with conc. HNO3/H2SO4 at 80 – 100°C forms which one of the following products?
(a) 1, 2-Dinitrobenzene
(b) 1, 3-Dinitrobenzene
(c) 1, 4-Dinitrobenzene
(d) 1, 2, 4-Trinitrobenzene
Answer
Answer: (b) 1, 3-Dinitrobenzene
Explanation:
NO2 is an m-directing group and hence, 1, 3-dinitrobenzene is formed.
Question 10.
The angle strain in cyclobutane is
(a) 24°44
(b) 29°16
(c) 19°22
(d) 9°44
Answer
Answer: (d) 9°44
Explanation:
According to Baeyers strain theory, the amount of the strain is directly proportional to the angle through which a valency bond has deviated from its normal position . i.e., Amount of deviation) in cyclobutane (d) = (109°28 – 90°)/(2) = 9°44
Question 11.
The lowest alkene, that is capable of exhibiting geometrical isomerism is
(a) Ethene
(b) But – 1- ene
(c) But – 2 – ene
(d) Propene.
Answer
Answer: (c) But – 2 – ene
Explanation:
The lowest alkene which is capable of exhibiting geometrical isomerism is 2-Butene
Question 12.
Presence of a nitro group in a benzene ring
(a) Activates the ring towards electrophilic substitution
(b) Renders the ring basic
(c) Deactivates the ring towards nucleophilic substitution
(d) Deactivates the ring towards electrophilic substitution
Answer
Answer: (d) Deactivates the ring towards electrophilic substitution
Explanation:
-NO2 group shows -M effect, so withdraws the electron density from the ring and hence deactivate the ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution.
Question 13.
A dibromo derivative of an alkane reacts with sodium metal to form an alicyclic hydrocarbon. The derivative is ______.
(a) 2, 2-dibromobutane
(b) 1, 1-dibromopropane
(c) 1, 4-dibromobutane
(d) 1, 2-dibromoethane
Answer
Answer: (c) 1, 4-dibromobutane
Explanation:
The derivative is 1, 4 dibromobutane. This on reaction with sodium metal gives cyclobutane.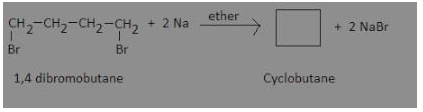
This reaction is an example of internal Wurtz reaction.
Question 14.
The position of double bond in alkenes can be located by :
(a) Hydrogenation of oil
(b) Ozonolysis
(c) Photolysis
(d) Hydration
Answer
Answer: (b) Ozonolysis
Explanation:
Ozonolysis is the cleavage of an alkene or alkyne with ozone to form organic compounds in which the multiple carbon-carbon bonds have been replaced by a double bond to oxygen. The outcome of the reaction depends on the type of multiple bonds being oxidized.
Bromine water can be also used to identify the position of a double bond. In this reaction, red-brown colour of bromine gets turned into coulorless indicating that there is a double bond.
Question 15.
The coal tar fraction which contains phenol is:
(a) Heavy Oil
(b) Light Oil
(c) Middle Oil
(d) Green Oil
Answer
Answer: (c) Middle Oil
Explanation:
The second fraction of coal-tar distillation which distills at 170°-230°C is called middle-oil or olic oil. It contains mainly phenol, naphthalene etc.
Question 16.
Which one of these is not true for benzene?
(a) There are three carbon-carbon single bonds and three carbon-carbon double bonds.
(b) Heat of hydrogenation of benzene is less than the theoretical value
(c) It forms only one type of mono substituted product
(d) The bond angle between carbon-carbon bonds is 120 Degree
Answer
Answer: (a) There are three carbon-carbon single bonds and three carbon-carbon double bonds.
Explanation:
There are three carbon-carbon single bonds and three carbon-carbon double bonds.
Question 17.
The catalyst used in Friedel – Crafts reaction is
(a) Aluminium Chloride
(b) Anhydrous Aluminium Chloride
(c) Ferric Chloride
(d) Copper .
Answer
Answer: (b) Anhydrous Aluminium Chloride
Explanation:
It is a catalyst-based electrophilic substitution reaction. Lewis acids like anhydrous AlCl3, anhydrous FeCl3, BF3 and BiCl3 can be used as catalysts. The catalyst facilitates more effective attack by the electrophile (R+, RCO+ etc.) on the benzene ring.
Question 18.
Alkyl halides react with dialkyl copper reagents to give?
(a) Alkanes
(b) Alkenes
(c) Hydrogen
(d) Carbon
Answer
Answer: (a) Alkanes
Explanation:
Alkyl halides react with dialkyl copper reagents to give Alkanes.
Question 19.
Hydrocarbon containing following bond is most reactive
(a) C = C
(b) C = C
(c) C-C
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (a) C = C
Explanation:
-C = C-is most reactive because sp-hybridization.
Question 20.
The compound C3H4 has a triple bond, which is indicated by its reaction with
(a) Bromine water
(b) Bayers reagent
(c) Fehling solution
(d) Ammonical silver nitrate
Answer
Answer: (d) Ammonical silver nitrate
Explanation:
CH3-C = C-H + AgNO3 ? CH3 -C = C-Ag
Propyne Ammonical Siver salt of Propyne














0 Comments:
Post a Comment