CBSE Class 11 Biology – MCQ and Online Tests – Unit 6 – Anatomy of Flowering Plants
Every year CBSE schools conducts Annual Assessment exams for 6,7,8,9,11th standards. These exams are very competitive to all the students. So our website provides online tests for all the 6,7,8,9,11th standard’s subjects. These tests are also very effective and useful for those who preparing for any competitive exams like Olympiad etc. It can boost their preparation level and confidence level by attempting these chapter wise online tests.
These online tests are based on latest CBSE syllabus. While attempting these our students can identify the weak lessons and continuously practice those lessons for attaining high marks. It also helps to revise the NCERT textbooks thoroughly.
CBSE Class 11 Biology – MCQ and Online Tests – Unit 6 – Anatomy of Flowering Plants
Question 1.
Walls of sclerenchyma are
(a) rigid
(b) lignified
(c) pectinised
(d) suberised
Answer
Answer: (b) lignified
Question 2.
Fusifrom initial cells of cambium from
(a) vascular rays
(b) tracheary elements
(c) ray parenchyma
(d) phloem parenchyma
Answer
Answer: (b) tracheary elements
Question 3.
Callose deposition is found in
(a) tracheids
(b) companion cells
(c) sieve areas
(d) phloem parenchyma
Answer
Answer: (c) sieve areas
Question 4.
Which of the following is not a feature of spring wood?
(a) Color of the wood is light.
(b) Density is less.
(c) Cambium is active.
(d) Lesser number of xylary elements.
Answer
Answer: (d) Lesser number of xylary elements.
Explanation:
Spring season produces a wood which has large number of xylary elements having vessels with wider cavities.
Question 5.
In a monocot leaf
(a) bulliform cells are absent from the eqidermis
(b) veins from a network
(c) mesophyll is well differentiated into palisade and spongy parenchyma
(d) mesophyll is not differentiated into palisade and spongy parenchyma
Answer
Answer: (d) mesophyll is not differentiated into palisade and spongy parenchyma
Question 6.
A.T.S. of a young dicot root can be distinguished from that of a young dicot stem by the presence of
(a) radial arrangement of xylem and phloem
(b) collateral arrangement of xylem and phloem
(c) interfascicular cambium
(d) intrafascicular cambium
Answer
Answer: (a) radial arrangement of xylem and phloem
Question 7.
Fusifrom initial cells of cambium from
(a) vascular rays
(b) tracheary elements
(c) ray parenchyma
(d) phloem parenchyma
Answer
Answer: (b) tracheary elements
Question 8.
Stem develops from
(a) radicle
(b) cotyledon
(c) mesocarp
(d) plumule
Answer
Answer: (d) plumule
Explanation:
Stem develops from plumule.
Question 9.
Stem grows in girth due to
(a) outer cortical
(b) epidermis
(c) vascular cambium
(d) phellogen
Answer
Answer: (c) vascular cambium
Explanation:
Stem increase in girth due to the activity of vascular cambium.
In this process, the outer cortical and epidermis layers gets broken.
This layer is replaced with new protective cell layer.
Question 10.
Which picture shows conjoint closed vascular bundles?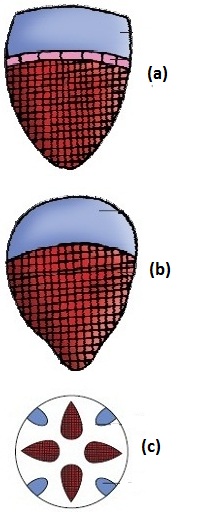
(d) None of these pictures shows conjoint closed vascular bundles.
Answer
Answer: (b)
Explanation: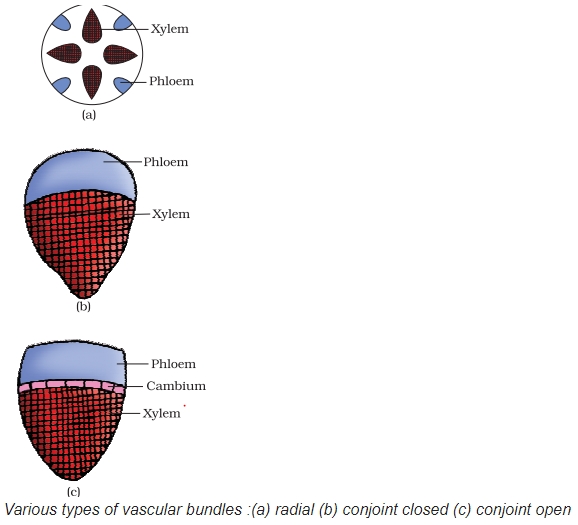
Question 11.
Pith is very well developed in
(a) monocot root and monocot srem
(b) monocot root and dicot root
(c) dicot root and monocot stem
(d) monocot root and dicot stem
Answer
Answer: (d) monocot root and dicot stem
Question 12.
Which of the following helps in the curling of the leaf surface?
(a) Bulliform cells
(b) Xylem tissue
(c) Palisade parenchyma
(d) Bundle sheath cells
Answer
Answer: (a) Bulliform cells
Explanation:
In grasses, adaxial epidermal cells along the veins modify themselves into large, empty, colorless cells. These are called bulliform cells.
When there is water stress leaves curl themselves inward to minimise water loss.
When the cells have absorbed water and are turgid, the leaf surface is exposed.
Question 13.
Vessels differ from tracheids
(a) in being living
(b) in being derived from a single cell
(c) in that they consist of vertical row of cells with cross walls dissolved
(d) in coducting water and minerals
Answer
Answer: (c) in that they consist of vertical row of cells with cross walls dissolved
Question 14.
Endodermis cells are rich in
(a) cellulose
(b) starch grains
(c) fibers
(d) resins and wax
Answer
Answer: (b) starch grains
Explanation:
Endodermis cells are rich in starch grains.
Question 15.
Quiescent centre is present in the
(a) apical meristem
(b) shoot meristem
(c) lateral meristem
(d) root meristem
Answer
Answer: (d) root meristem
Question 16.
Closed vascular bundles lacks
(a) pith
(b) xylem
(c) cambium
(d) xylem vessels
Answer
Answer: (c) cambium
Explanation:
Picture of closed conjoint vascular bundles.
Question 17.
Closed vascular bundles lacks
(a) pith
(b) xylem
(c) cambium
(d) xylem vessels
Answer
Answer: (c) cambium
Question 18.
After the secondary growth, the oldest layer of secondary phloem in a dicot stem is located
(a) just outside the vascular cambium
(b) just inside the vascular cambium
(c) just inside the vascular phloem
(d) just outside the secondary xylem
Answer
Answer: (c) just inside the vascular phloem
Question 19.
The innermost layer of cortex which shows casparian thickenings in its cells is called as
(a) epidermis
(b) endodermis
(c) pericycle
(d) exodermis
Answer
Answer: (b) endodermis
Question 20.
Which of the following is true about heartwood?
(a) They are dead but gives mechanical support to stem.
(b) They are light in color.
(c) They conduct water and minerals.
(d) 1 and 3
Answer
Answer: (a) They are dead but gives mechanical support to stem.
Explanation:
Heartwood is dead and have non-conducting elements.













0 Comments:
Post a Comment