CBSE Class 11 Maths – MCQ and Online Tests – Unit 6 – Linear Inequalities
Every year CBSE schools conducts Annual Assessment exams for 6,7,8,9,11th standards. These exams are very competitive to all the students. So our website provides online tests for all the 6,7,8,9,11th standard’s subjects. These tests are also very effective and useful for those who preparing for any competitive exams like Olympiad etc. It can boost their preparation level and confidence level by attempting these chapter wise online tests.
These online tests are based on latest CBSE syllabus. While attempting these our students can identify the weak lessons and continuously practice those lessons for attaining high marks. It also helps to revise the NCERT textbooks thoroughly.
CBSE Class 11 Maths – MCQ and Online Tests – Unit 6 – Linear Inequalities
Question 1.
If x² = -4 then the value of x is
(a) (-2, 2)
(b) (-2, 8)
(c) (2, 8)
(d) No solution
Answer
Answer: (d) No solution
Hint:
Given, x² = -4
Since LHS = 0 and RHS < 0
So, No solution is possible.
Question 2.
Solve: |x – 3| < 5
(a) (2, 8)
(b) (-2, 8)
(c) (8, 2)
(d) (8, -2)
Answer
Answer: (b) (-2, 8)
Hint:
Given, |x – 3| < 5
? -5 < (x – 3) < 5
? -5 + 3 < x < 5 + 3
? -2 < x < 8
? x ? (-2, 8)
Question 3.
If x² = 4 then the value of x is
(a) -2
(b) 2
(c) -2, 2
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) -2, 2
Hint:
Given, x² = 4
? x² – 4 = 0
? (x – 2)×(x + 2) = 0
? x = -2, 2
Question 4.
Solve: (x + 1)² + (x² + 3x + 2)² = 0
(a) x = -1, -2
(b) x = -1
(c) x = -2
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) x = -1
Hint:
Given, (x + 1)² + (x² + 3x + 2)² = 0
This is true when each term is equal to zero simultaneously,
So, (x + 1)² = 0 and (x² + 3x + 2)² = 0
? x + 1 = 0 and x² + 3x + 2 = 0
? x = -1, and x = -1, -2
Now, the common solution is x = -1
So, solution of the equation is x = -1
Question 5.
If (x + 3)/(x – 2) > 1/2 then x lies in the interval
(a) (-8, 8)
(b) (8, 8)
(c) (8, -8)
(d) (8, 8)
Answer
Answer: (a) (-8, 8)
Hint:
Given,
(x + 3)/(x – 2) > 1/2
? 2(x + 3) > x – 2
? 2x + 6 > x – 2
? 2x – x > -2 – 6
? x > -8
? x ? (-8, 8)
Question 6.
The region of the XOY-plane represented by the inequalities x = 6, y = 2, 2x + y = 10 is
(a) unbounded
(b) a polygon
(c) none of these
(d) exterior of a triangle
Answer
Answer: (c) none of these
Hint:
Given inequalities x = 6, y = 2, 2x + y = 10
Now take x = 6, y = 2 and 2x + y = 10
when x = 0, y = 10
when y = 0, x = 5
So, the points are A(6, 2), B(0, 10) and C(5, 0)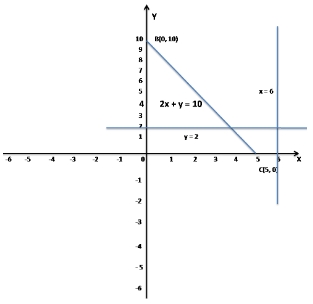
So, the region of the XOY-plane represented by the inequalities x = 6, y = 2, 2x + y = 10 is not defined.
Question 7.
The interval in which f(x) = (x – 1) × (x – 2) × (x – 3) is negative is
(a) x > 2
(b) 2 < x and x < 1
(c) 2 < x < 1 and x < 3
(d) 2 < x < 3 and x < 1
Answer
Answer: (d) 2 < x < 3 and x < 1
Hint:
Given, f(x) = (x – 1) × (x – 2) × (x – 3) has all factors with odd powers.
So, put them zero
i.e. x – 1 = 0, x – 2 = 0, x – 3 = 0
? x = 1, 2, 3
Now, f(x) < 0 when 2 < x < 3 and x < 1
Question 8.
If -2 < 2x – 1 < 2 then the value of x lies in the interval
(a) (1/2, 3/2)
(b) (-1/2, 3/2)
(c) (3/2, 1/2)
(d) (3/2, -1/2)
Answer
Answer: (b) (-1/2, 3/2)
Hint:
Given, -2 < 2x – 1 < 2
? -2 + 1 < 2x < 2 + 1
? -1 < 2x < 3
? -1/2 < x < 3/2
? x ?(-1/2, 3/2)
Question 9.
Sum of two rational numbers is ______ number.
(a) rational
(b) irrational
(c) Integer
(d) Both 1, 2 and 3
Answer
Answer: (a) rational
Hint:
The sum of two rational numbers is a rational number.
Ex: Let two rational numbers are 1/2 and 1/3
Now, 1/2 + 1/3 = 5/6 which is a rational number.
Question 10.
If x² = -4 then the value of x is
(a) (-2, 2)
(b) (-2, 8)
(c) (2, 8)
(d) No solution
Answer
Answer: (d) No solution
Hint:
Given, x² = -4
Since LHS = 0 and RHS < 0
So, No solution is possible.
Question 11.
The solution of |2/(x – 4)| > 1 where x ? 4 is
(a) (2, 6)
(b) (2, 4) ? (4, 6)
(c) (2, 4) ? (4, 8)
(d) (-8, 4) ? (4, 6)
Answer
Answer: (b) (2, 4) ? (4, 6)
Hint:
Given, |2/(x – 4)| > 1
? 2/|x – 4| > 1
? 2 > |x – 4|
? |x – 4| < 2
? -2 < x – 4 < 2
? -2 + 4 < x < 2 + 4
? 2 < x < 6
? x ? (2, 6) , where x ? 4
? x ? (2, 4) ? (4, 6)
Question 12.
If (|x| – 1)/(|x| – 2) ?= 0, x ? R, x ?± 2 then the interval of x is
(a) (-8, -2) ? [-1, 1]
(b) [-1, 1] ? (2, 8)
(c) (-8, -2) ? (2, 8)
(d) (-8, -2) ? [-1, 1] ? (2, 8)
Answer
Answer: (d) (-8, -2) ? [-1, 1] ? (2, 8)
Hint:
Given, (|x| – 1)/(|x| – 2) ?= 0
Let y = |x|
So, (y – 1)/(y – 2) ?= 0
? y = 1 or y > 2
? |x| = 1 or |x| > 2
? (-1 = x = 1) or (x < -2 or x > 2)
? x ? [-1, 1] ? (-8, -2) ? (2, 8)
Hence the solution set is:
x ? (-8, -2) ? [-1, 1] ? (2, 8)
Question 13.
The solution of the -12 < (4 -3x)/(-5) < 2 is
(a) 56/3 < x < 14/3
(b) -56/3 < x < -14/3
(c) 56/3 < x < -14/3
(d) -56/3 < x < 14/3
Answer
Answer: (d) -56/3 < x < 14/3
Hint:
Given inequality is :
-12 < (4 -3x)/(-5) < 2
? -2 < (4-3x)/5 < 12
? -2 × 5 < 4 – 3x < 12 × 5
? -10 < 4 – 3x < 60
? -10 – 4 < -3x < 60-4
? -14 < -3x < 56
? -56 < 3x < 14
? -56/3 < x < 14/3
Question 14.
The solution of the 15 < 3(x – 2)/5 < 0 is
(a) 27 < x < 2
(b) 27 < x < -2
(c) -27 < x < 2
(d) -27 < x < -2
Answer
Answer: (a) 27 < x < 2
Hint:
Given inequality is:
15 < 3(x-2)/5 < 0
? 15 × 5 < 3(x-2) < 0 × 5
? 75 < 3(x-2) < 0
? 75/3 < x-2 < 0
? 25 < x-2 < 0
? 25 +2 < x <0+2
? 27 < x < 2
Question 15.
Solve: 1 = |x – 1| = 3
(a) [-2, 0]
(b) [2, 4]
(c) [-2, 0] ? [2, 4]
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) [-2, 0] ? [2, 4]
Hint:
Given, 1 = |x – 1| = 3
? -3 = (x – 1) = -1 or 1 = (x – 1) = 3
i.e. the distance covered is between 1 unit to 3 units
? -2 = x = 0 or 2 = x = 4
Hence, the solution set of the given inequality is
x ? [-2, 0] ? [2, 4]
Question 16.
The graph of the inequations x = 0, y = 0, 3x + 4y = 12 is
(a) none of these
(b) interior of a triangle including the points on the sides
(c) in the 2nd quadrant
(d) exterior of a triangle
Answer
Answer: (b) interior of a triangle including the points on the sides
Hint:
Given inequalities x = 0, y = 0, 3x + 4y = 12
Now take x = 0, y = 0 and 3x + 4y = 12
when x = 0, y = 3
when y = 0, x = 4
So, the points are A(0, 0), B(0, 3) and C(4, 0)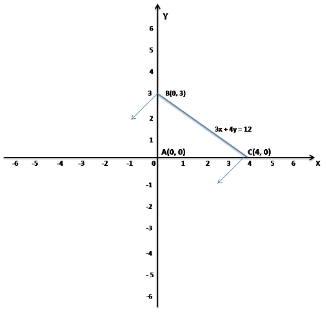
So, the graph of the inequations x = 0, y = 0, 3x + 4y = 12 is interior of a triangle including the points on the sides.
Question 17.
If |x| < 5 then the value of x lies in the interval
(a) (-8, -5)
(b) (8, 5)
(c) (-5, 8)
(d) (-5, 5)
Answer
Answer: (d) (-5, 5)
Hint:
Given, |x| < 5
It means that x is the number which is at distance less than 5 from 0
Hence, -5 < x < 5
? x ? (-5, 5)
Question 18.
Solve: f(x) = {(x – 1)×(2 – x)}/(x – 3) = 0
(a) (-8, 1] ? (2, 8)
(b) (-8, 1] ? (2, 3)
(c) (-8, 1] ? (3, 8)
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) (-8, 1] ? (2, 3)
Hint:
Given, f(x) = {(x – 1)×(2 – x)}/(x – 3) = 0
or f(x) = -{(x – 1)×(2 – x)}/(x – 3)
which gives x – 3 ? 0
? x ? 3![]()
Using number line rule as shown in the figure,
which gives f(x) = 0 when x = 1 or 2 = x < 3
i.e. x ? (-8, 1] ? (2, 3)
Question 19.
The solution of the inequality |x – 1| < 2 is
(a) (1, 8)
(b) (-1, 3)
(c) (1, -3)
(d) (8, 1)
Answer
Answer: (b) (-1, 3)
Hint:
Given, |x – 1| < 2
? -2 < x – 1 < 2
? -2 + 1 < x < 2 + 1
? -1 < x < 3
? x ? (-1, 3)
Question 20.
If | x – 1| > 5, then
(a) x?(-8, -4)?(6, 8]
(b) x?[6, 8)
(c) x?(6, 8)
(d) x?(-8, -4)?(6, 8)
Answer
Answer: (d) x?(-8, -4)?(6, 8)
Hint:
Given |x-1| >5
Case 1:
(x – 1) > 5
? x > 6
? x ? (6,8)
Case 2:
-(x – 1) > 5
? -x + 1 > 5
? -x > 4
? x < -4
? x ? (-8, -4)
So the range of x is (-8, -4)?(6, 8)














0 Comments:
Post a Comment