CBSE Class 11 Chemistry – MCQ and Online Tests – Unit 9 – Hydrogen
Every year CBSE schools conducts Annual Assessment exams for 6,7,8,9,11th standards. These exams are very competitive to all the students. So our website provides online tests for all the 6,7,8,9,11th standard’s subjects. These tests are also very effective and useful for those who preparing for any competitive exams like Olympiad etc. It can boost their preparation level and confidence level by attempting these chapter wise online tests.
These online tests are based on latest CBSE syllabus. While attempting these our students can identify the weak lessons and continuously practice those lessons for attaining high marks. It also helps to revise the NCERT textbooks thoroughly.
CBSE Class 11 Chemistry – MCQ and Online Tests – Unit 9 – Hydrogen
Question 1.
H2O2 used in rocket has the concentration:
(a) 50%
(b) 90%
(c) 70%
(d) 30%
Answer
Answer: (b) 90%
Explanation:
H2O2 is used as an oxidant for rocket fuel. Usually, 90% concentration of H2O2 is used.
Question 2.
Which of the following hydrides are generally nonstochiometric in nature?
(a) Ionic Hydrides
(b) Molecular Hydrides
(c) Interstitial Hydrides
(d) All of the Above.
Answer
Answer: (c) Interstitial Hydrides
Explanation:
Interstitial hydrides are non- stoichiometric hydrides and thus deficit in hydrogen. Transition and inner transition elements at relevant temperature absorb hydrogen into the interstices of their lattices to yield metal like hydrides.
Question 3.
What is the product of the reaction of H2O2 with Cl2?
(a) O2 + HOCl
(b) HCl + O2
(c) H2O + HCl
(d) HCl + H2
Answer
Answer: (b) HCl + O2
Explanation:
H2O2 + Cl2 ? 2HCl + O2
Question 4.
Water shows anomalous behavior between
(a) 0 to 4°C
(b) 0 to 5°C
(c) 0 to -4°C
(d) 4 to 0°C
Answer
Answer: (a) 0 to 4°C
Explanation:
Water show a wide range of anomalies compared to similar liquids or hydrides of other group 16 elements. One of the most talked-about anomalies is the formation of ice from liquid water and how the density changes when we cool the water.
O is a small atom and highly electronegative compared to Hydrogen. So O attracts the covalent clouds of O-H towards itself, thus making water a polar molecule. The hydrogen bonding in water molecules causes high boiling point and liquid state compared to other hydrides of group 16.
When we cool water from higher temperature, the density steadily decreases. At 4 degree C it is the highest. But below 4 degree C, The H-bonds break between the molecules and the molecules get drifted further apart, the volume increases and density decreases. The crystalline form of water is ice. At atmospheric pressure ice crystallises in the hexagonal form, but at very low temperatures it condenses to cubic form leaving gap between the structures, thus increasing the volume again.
Density of ice is less than that of water. Therefore, an ice cube floats on water. In winter season ice formed on the surface of a lake provides thermal insulation which ensures the survival of the aquatic life.
Question 5.
Which of the following statements regarding hydrogen peroxide is/ are incorrect?
(a) As aerating agent in production of sponge rubber
(b) As an antichlor
(c) For restoring white colour of blackened lead painting
(d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All of the above
Explanation:
H2O2 show all these properties
Question 6.
Water gas is mixture of hydrogen H2 and
(a) CO
(b) CO2
(c) Cl2
(d) SO2
Answer
Answer: (a) CO
Explanation:
Water gas is a combustion fuel containing carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen gas (H2). Water gas is made by passing steam over heated hydrocarbons.
Question 7.
Pure H2O2 is :
(a) Semi – solid
(b) Liquid
(c) Solid
(d) Gas
Answer
Answer: (b) Liquid
Explanation:
Hydrogen peroxide is the simplest kind of peroxide available (oxygen-oxygen single bond). It is a colourless liquid and is used in aqueous solution for safety reasons. It acts as a bleaching agent and is also used as a disinfectant. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide is a very reactive oxygen species and is used as a propellant in rocketry. The chemical formula for hydrogen peroxide is H2O2.
Question 8.
The freezing point of heavy water is
(a) 0°C
(b) 3.8°C
(c) 4°C
(d) 1°C
Answer
Answer: (b) 3.8°C
Question 9.
Hydrogen has isotopes
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer
Answer: (c) 4
Explanation:
Hydrogen has three main isotopes; Protium (1H), deuterium (²H) and tritium (³H). These isotopes form naturally in nature. Protium and deuterium are stable. Tritium is radioactive and has a half-life of about 12 years. Scientists have created four other hydrogen isotopes (4H to 7H), but these isotopes are very unstable and do not exist naturally.
The main isotopes of hydrogen are unique because they are the only isotopes that have a name.
Question 10.
The freezing point of heavy water is
(a) 0°C
(b) 3.8°C
(c) 4°C
(d) 1°C
Answer
Answer: (b) 3.8°C
Question 11.
Pure H2O2 is:
(a) Semi – solid
(b) Liquid
(c) Solid
(d) Gas
Answer
Answer: (b) Liquid
Explanation:
Hydrogen peroxide is the simplest kind of peroxide available (oxygen-oxygen single bond). It is a colourless liquid and is used in aqueous solution for safety reasons. It acts as a bleaching agent and is also used as a disinfectant. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide is a very reactive oxygen species and is used as a propellant in rocketry. The chemical formula for hydrogen peroxide is H2O2.
Question 12.
_________________ on water decolourises H2O2
(a) O3
(b) Acidic KMnO4 solution
(c) Black Suspension of Lead Sulphide(PbS)
(d) None of these.
Answer
Answer: (c) Black Suspension of Lead Sulphide(PbS)
Explanation:
Lead sulphide (black suspension) on reaction with hydrogen peroxide forms lead sulphate and water. Lead sulphate as well as water are colourless, therefore lead sulphite decolourises on addition of hydrogen peroxide.
PbS(s) + 4H2O2 (aq) ? PbSO4 (s) + 4H2O (aq)
Question 13.
The volume of 10 volume H2O2 required to liberate 500 ml of O2 at S.T.P. is :
(a) 25 ml
(b) 50 ml
(c) 100 ml
(d) 125 ml
Answer
Answer: (b) 50 ml
Explanation:
As 10 ml of oxygen is obtained at STP from H2O2 = 1 ml
Therefore, 500 ml of O2 is obtained at STP = 50 ml
Question 14.
Hydrogen is most __________ element in the universe.
(a) Abundant
(b) None
(c) Both
(d) Consumer
Answer
Answer: (a) Abundant
Explanation:
Hydrogen is considered as the most common and abundant element. The element Hydrogen has only one proton and one electron and is the only element which has no neutrons. Therefore it is considered as the simplest element in the universe and gives a valid reason for it to be the most abundant and common element in the universe. As per estimation from the Jefferson Lab, approximately 90 percent of the visible universe is framed by Hydrogen proving that being in the simplest form, this element is the most common and abundant element in the universe.
Question 15.
Atomic hydrogen is called
(a) Protium
(b) Deutrium
(c) Nascent Hydrogen
(d) Tritium
Answer
Answer: (c) Nascent Hydrogen
Explanation:
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the baryonic mass of the universe.
In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (called “atomic hydrogen”) are extremely rare. Instead, a hydrogen atom tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with another hydrogen atom to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. “Atomic hydrogen” and “hydrogen atom”
Question 16.
Hydrogen is a good __________ agent.
(a) Oxidizing
(b) Reducing
(c) Acidic
(d) Basic
Answer
Answer: (b) Reducing
Explanation:
Hydrogen acts as a good reducing agent means, when hydrogen gas is passed over hot metallic oxides of copper, lead, iron, etc. it removes oxygen from them and thus reduces them to their corresponding metal. Let us consider the following example, in each of which metallic oxide react with hydrogen. Metallic oxide act as oxidizing agents and hydrogen acts as a reducing agent.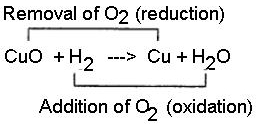
Question 17.
Atomic hydrogen is called
(a) Protium
(b) Deutrium
(c) Nascent Hydrogen
(d) Tritium
Answer
Answer: (c) Nascent Hydrogen
Explanation:
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the baryonic mass of the universe.
In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (called “atomic hydrogen”) are extremely rare. Instead, a hydrogen atom tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with another hydrogen atom to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. “Atomic hydrogen” and “hydrogen atom”
Question 18.
The volume strength of 1.5 NH2O2 solution is :
(a) 4.8
(b) 5.2
(c) 8.8
(d) 8.4
Answer
Answer: (d) 8.4
Explanation:
Strength =Normality ×Equivalent Weight of H2O2
= 1.5N × 1.7gL-1 = 25.5gL-1
2H2O2 ? 2H2O + O2
68g 22400 mLat STP
68 g of H2O gives = 22400 mL of O2 at STP
25.5 gH2O2 gives = 2240068 × 25.5 = 8400 mL of O2 at STP
25.5g of H2O2 is present in 1000 mL of H2O2 solution
1000 mL of H2O2 gives 8400 mL of O2 at STP
1 mL of H2O2 gives 84001000 mL of O2 at STP
= 8.4mL of O2
Hence, volume strength of 1.5NH2O2 = 8.4 volume.
Or mass of H2O2 in 1.5N solution
= Equivalent Weight of H2O2 × 1.5N
= 17 × 1.5 = 25.5 g/L
Hence, volume strength of 1.5NH2O2 solution
= 22.4 × 25.568 = 8.4














0 Comments:
Post a Comment