CBSE Class 11 Chemistry – MCQ and Online Tests – Unit 4 – Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Every year CBSE schools conducts Annual Assessment exams for 6,7,8,9,11th standards. These exams are very competitive to all the students. So our website provides online tests for all the 6,7,8,9,11th standard’s subjects. These tests are also very effective and useful for those who preparing for any competitive exams like Olympiad etc. It can boost their preparation level and confidence level by attempting these chapter wise online tests.
These online tests are based on latest CBSE syllabus. While attempting these our students can identify the weak lessons and continuously practice those lessons for attaining high marks. It also helps to revise the NCERT textbooks thoroughly.
CBSE Class 11 Chemistry – MCQ and Online Tests – Unit 4 – Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Question 1.
An atom of an element A has three electrons in its outermost orbit and that of B has six electrons in its outermost orbit. The formula of the compound between these two will be
(a) A3B6
(b) A2B3
(c) A3B2
(d) A2B
Answer
Answer: (b) A2B3
Explanation:
A has 3 electrons in outermost orbit and B has 6 electrons in its outermost orbits. So A can give three electrons to complete its octet and B needs 2 electrons to complete its octet. So 2 atoms of A will release 6 electrons and 3 atoms of B will need six electrons to complete their octet
So, the formula will be A2?B3
Question 2.
The maximum number of hydrogen bonds that a molecule of water can have is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
Answer: (d) 4
Explanation:
Each water molecule can form a maximum of four hydrogen bonds with neighboring water molecules. The two hydrogens of the water molecule can form hydrogen bonds with other oxygens in ice, and the two lone pair of electrons on oxygen of the water molecule can attract other hydrogens in ice. Hence, 4 possible hydrogen bonds.
Question 3.
The hybrid state of sulphur in SO2 molecule is :
(a) sp²
(b) sp³
(c) sp
(d) sp³d
Answer
Answer: (a) sp²
Explanation:
The hybridisation of sulphur in SO2 is sp². Sulphur atom has one lone pair of electrons and two bonding domains. Bond angle is <120° and molecular geometry is V-shape, bent or angular
Question 4.
Which one of the following does not have sp² hybridised carbon?
(a) Acetone
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Acetonitrile
(d) Acetamide
Answer
Answer: (c) Acetonitrile
Explanation:
Acetonitrile does not contain sp² hybridized carbon.
Question 5.
Among the following mixtures, dipole-dipole as the major interaction, is present in
(a) benzene and ethanol
(b) acetonitrile and acetone
(c) KCl and water
(d) benzene and carbon tetrachloride
Answer
Answer: (b) acetonitrile and acetone
Explanation:
Dipole-dipole interactions occur among the polar molecules. Polar molecules have permanent dipoles. The positive pole of one molecule is thus attracted by the negative pole of the other molecule. The magnitude of dipole-dipole forces in different polar molecules is predicted on the basis of the polarity of the molecules, which in turn depends upon the electro negativities of the atoms present in the molecule and the geometry of the molecule (in case of polyatomic molecules, containing more than two atoms in a molecule).
Question 6.
The value of n in the molecular formula BenAl2Si6O18 is
(a) 3
(b) 5
(c) 7
(d) 9
Answer
Answer: (a) 3
Explanation:
BenAl2Si6O18
The oxidation states of each element
Be = +2
Al = +3
Si = +4
O = -2
(2n) + (3 × 2) + (4 + 6) + (-2 × 18) = 0
or 2n + 30 – 36 = 0
or 2n = 6
or n = 3
Question 7.
Which of the following types of hybridisation leads to three dimensional geometry of bonds around the carbon atom?
(a) sp
(b) sp²
(c) sp³
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) sp²
Explanation:
sp² hybrid structures have trigonal planar geometry, which is two dimensional.
Question 8.
The bond length between hybridised carbon atom and other carbon atom is minimum in
(a) Propane
(b) Butane
(c) Propene
(d) Propyne
Answer
Answer: (d) Propyne
Explanation:
The C – C bond length = 1.54 Å, C = C bond length = 1.34 Å and C = C bond length = 1.20 Å.
Since propyne has a triple bond, therefore it has minimum bond length.
Question 9.
The number of nodal planes present in s × s antibonding orbitals is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 0
(d) 3
Answer
Answer: (a) 1
Explanation:
In an antibonding molecular orbital, most of the electron density is located away from the space between the nuclei, as a result of which there is a nodal plane (i.e, a plane at which the electron density is zero) between the nuclei.
Question 10.
The number of types of bonds between two carbon atoms in calcium carbide is
(a) Two sigma, two pi
(b) One sigma, two pi
(c) One sigma, one pi
(d) Two sigma, one pi
Answer
Answer: (b) One sigma, two pi
Explanation:
A single bond between two atoms is always considered as sigma bond.
A double bond between two atoms is always considered as one sigma and one pi bond
A triple bond between two atoms is always considered as one sigma bond and two pi bonds.
So according to the given structure CaC2 (Calcium carbide) has 1 sigma and 2 pi bonds
Question 11.
Based on lattice enthalpy and other considerations which one the following alkali metals chlorides is expected to have the higher melting point?
(a) RbCl
(b) KCl
(c) NaCl
(d) LiCl
Answer
Answer: (c) NaCl
Explanation:
The highest melting point will be NaCl, it is because, the lattice energy decreases as the size of alkali metal increases so going down the group the melting point decreases, but due to the covalent bonding in LiCl, its melting point is lower than NaCl and so NaCl is expected to have maximum melting point in the alkali chlorides.?
Question 12.
Dipole-induced dipole interactions are present in which of the following pairs?
(a) H2O and alcohol
(b) Cl2 and CCl4
(c) HCl and He atoms
(d) SiF4 and He atoms
Answer
Answer: (c) HCl and He atoms
Explanation:
HCl is polar (µ ? 0) and He is non-polar (µ = 0) gives dipole-induced dipole interaction.
Question 13.
The outer orbitals of C in ethene molecule can be considered to be hybridized to give three equivalent sp² orbitals. The total number of sigma (s) and pi (p) bonds in ethene molecule is
(a) 1 sigma (s) and 2 pi (p) bonds
(b) 3 sigma (s) and 2 pi (p) bonds
(c) 4 sigma (s) and 1 pi (p) bonds
(d) 5 sigma (s) and 1 pi (p) bonds
Answer
Answer: (d) 5 sigma (s) and 1 pi (p) bonds
Explanation:
According to valence bond theory, two atoms form a covalent bond through the overlap of individual half-filled valence atomic orbitals, each containing one unpaired electron. In ethene, each hydrogen atom has one unpaired electron and each carbon is sp² hybridized with one electron each sp² orbital. The fourth electron is in the p orbital that will form the pi bond. The bond order for ethene is simply the number of bonds between each atom: the carbon-carbon bond has a bond order of two, and each carbon-hydrogen bond has a bond order of one.
Question 14.
Which of the following is a linear molecule?
(a) ClO2
(b) CO2
(c) NO2
(d) SO2
Answer
Answer: (b) CO2
Explanation:
The steric number of central atom of a linear molecule is two. It has two bonded atoms and zero lone pair. All the molecules have two bonded atoms. Thus, we need to work out the number of lone pairs.
In ClO2, the central atom Cl has 7 valence electrons. Four are used up to form 4 bonds with O atoms. Three are non-bonding electrons. Thus, along with an odd electron, it has a lone pair.
In CO2, the central C atom has 4 valence electrons. All are used up to form four bonds with O atoms. Thus, it has zero lone pair.
In NO2, the central N atom has 5 valence electrons. Four are used up to form bonds with oxygen atoms. Thus, one electron is left as an odd electron.
In SO2, the central S atom has 6 valence electrons. Four are used up to form bonds with oxygen atoms. Two nonbonding electrons form one lone pair.
Question 15.
Among the following mixtures, dipole-dipole as the major interaction, is present in
(a) benzene and ethanol
(b) acetonitrile and acetone
(c) KCl and water
(d) benzene and carbon tetrachloride
Answer
Answer: (b) acetonitrile and acetone
Explanation:
Dipole-dipole interactions occur among the polar molecules. Polar molecules have permanent dipoles. The positive pole of one molecule is thus attracted by the negative pole of the other molecule. The magnitude of dipole-dipole forces in different polar molecules is predicted on the basis of the polarity of the molecules, which in turn depends upon the electro negativities of the atoms present in the molecule and the geometry of the molecule (in case of polyatomic molecules, containing more than two atoms in a molecule).
Question 16.
The charge/size ratio of a cation determines its polarizing power. Which one of the following sequences represents the increasing order of the polarizing order of the polarizing power of the cationic species, K+, Ca++, Mg2+, Be2+?
(a) Ca2+ < Mg2+ < Be+ < K+
(b) Mg2+ < Be2+ < K+ < Ca2+
(c) Be2+ < K+ < Ca2+ < Mg2+
(d) K+ < Ca2+ < Mg2+ < Be2+
Answer
Answer: (d) K+ < Ca2+ < Mg2+ < Be2+
Explanation:
High charge and small size of the cations increases polarisation.
As the size of the given cations decreases as
K+ > Ca2+ > Mg2+ > Be2+
Hence, polarising power decreases as K+ < Ca2+ < Mg2+ < Be2+
Question 17.
The species having pyramidal shape is
(a) SO3
(b) BrF3
(c) SiO32-
(d) OSF2
Answer
Answer: (d) OSF2
Explanation:
The species having a pyramidal shape according to VSEPR theory is OSF2. The central S atom has 3 bonding domains (one S = O double bond and two S-F single bonds) and one lone pair of electrons.
The electron pair geometry is tetrahedral and molecular geometry is pyramidal. This is similar to the ammonia molecule.
Question 18.
The structure of IF7 is
(a) Pentagonal bipyramid
(b) Square pyramid
(c) Trigonal bipyramid
(d) Octahedral
Answer
Answer: (a) Pentagonal bipyramid
Explanation:
IF7 Hybridization is sp³d³
Structure is Pentagonal bipyramidal.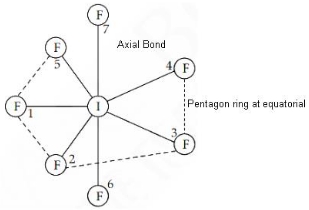
Question 19.
Which of the following will have the lowest boiling point?
(a) 2-MethylButane
(b) 2-MethylPropane
(c) 2,2-Dimethylpropane
(d) n-Pentane
Answer
Answer: (d) n-Pentane
Explanation:
Boiling point increases with increase in molecular mass. For the compounds with the same molecular mass, boiling point decreases with an increase in branching.
The molecular mass of 2-Methylbutane: 72 g mol-1
The molecular mass of 2-Methylpropane: 58 g mol-1
The molecular mass of 2, 2-Dimethylpropane: 72 g mol-1
The molecular mass of 2-Methylbutane: 72 g mol-1
2-Methylpropane has the lowest molecular mass among all of the given compounds.
Thus, 2-Methylpropane has the lowest boiling point among the given options.
Question 20.
Among the following the maximum covalent character is shown by the compound
(a) MgCl2
(b) FeCl2
(c) SnCl2
(d) AlCl3
Answer
Answer: (d) AlCl3
Explanation:
We know that, extent of polarisation ? covalent character in ionic bond. Fajans rule states that the polarising power of cation increases, with increase in magnitude of positive charge on the cation Therefore, polarising power ? charge of cation.
The polarising power of cation increases with the decrease in the size of a cation. Therefore, polarising (power) ? (1)/ (size of cation)
Here the AlCl3 is satisfying the above two conditions i.e., Al is in +3 oxidation state and also has small size. So it has more covalent character.














0 Comments:
Post a Comment